Routers function the same way, may they be used at home or in large businesses. Essentially, their role is to connect one network to another right? That’s where the name was derived from, “Router”, to route from one place to another.
ASIDE FROM THIS, A ROUTER HAS OTHER FUNCTIONS.
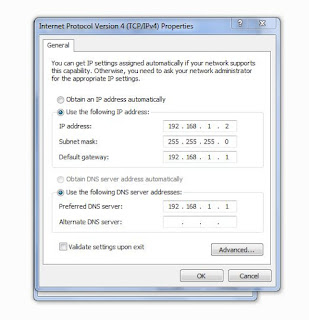
A router functions as your computer’s “GATEWAY” to other networks. Have you ever noticed that when you are configuring your computer’s IP address statically you are required to fill out a couple of configurations?
1) The IP address
2) The Subnet Mask
3) The Default Gateway
4) The DNS Server
The “Default Gateway” is most of the time, if not always, the IP Address of your router.
For example you input 192.168.1.1 as your default gateway, you just then instructed your devices (computers) that whenever they want to reach an address that they do not know (meaning, the address is not on their network), throw the data on your default gateway which is 192.168.1.1. That is how we are able to communicate out of our networks to other networks and most of the time, to the internet.
The router also serves as our DHCP SERVER. DCHP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. This functionality allows our routers to distribute IP addresses to any clients connected to the network.
THIS IS BENEFICIAL IN TWO WAYS
1. If you have hundreds of devices in your network, you won’t have to go and configure them one at a time statically.
2. You avoid having duplicate IP addresses in your network since the router is the one assigning them.
Another function of the router is to be our Port Address Translator (PAT) or Network Address Translator (NAT). Technically, the IP addresses that we have in our internal networks won’t work when we would like to communicate to the internet. That’s why we have routers to help us get there.
When for example you wanted to open a Facebook page. Before your packet (request) leaves the router, your IP address must be first converted to an IP that is publicly routable. And what address would that be? It is the address that was assigned to you by your ISP – Internet Service Provider.
Suppose you have fifty devices inside your network, that would mean that you will have to have fifty internal IP addresses right? But every time someone connects outside your network, the address always will be converted to that one external IP address. That’s why when you launch a cyber-attack, they can always trace it back to your external IP as the source.
To know your internal IP address, just open a Command Prompt and type “ipconfig /all” without the quotes.
To know your external IP address, go to google.com, then type “What is My IP”.
Lastly, our routers function as our DNS SERVER. DNS means Domain Name Service. This functionality is simple to explain. Remember that our devices cannot understand human language? They always have to convert it to decimals and binary. So, if we put Facebook.com in our address bar, the computer does not know what that means and will not look for the word “Facebook.com” in the internet. Instead, the DNS role would then have to convert “Facebook.com” to an IP Address that the computer would understand.
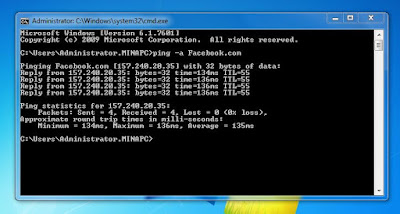
To know the IP addresses of websites, open a Command Prompt, type “ping –a” followed by the website of your choosing. In this case, one of Facebook’s IP is 157.240.20.35.
To know the IP addresses of websites, open a Command Prompt, type “ping –a” followed by the website of your choosing. In this case, one of Facebook’s IP is 157.240.20.35.



I want to use this opportunity to thank cybergoldenhacker professional service for a job well done ,I don't know its possible to spy on my partners phone remotely. If you need to check your spouse phone remotely without touching it contact : cybergoldenhacker at gmail dot com
ReplyDelete